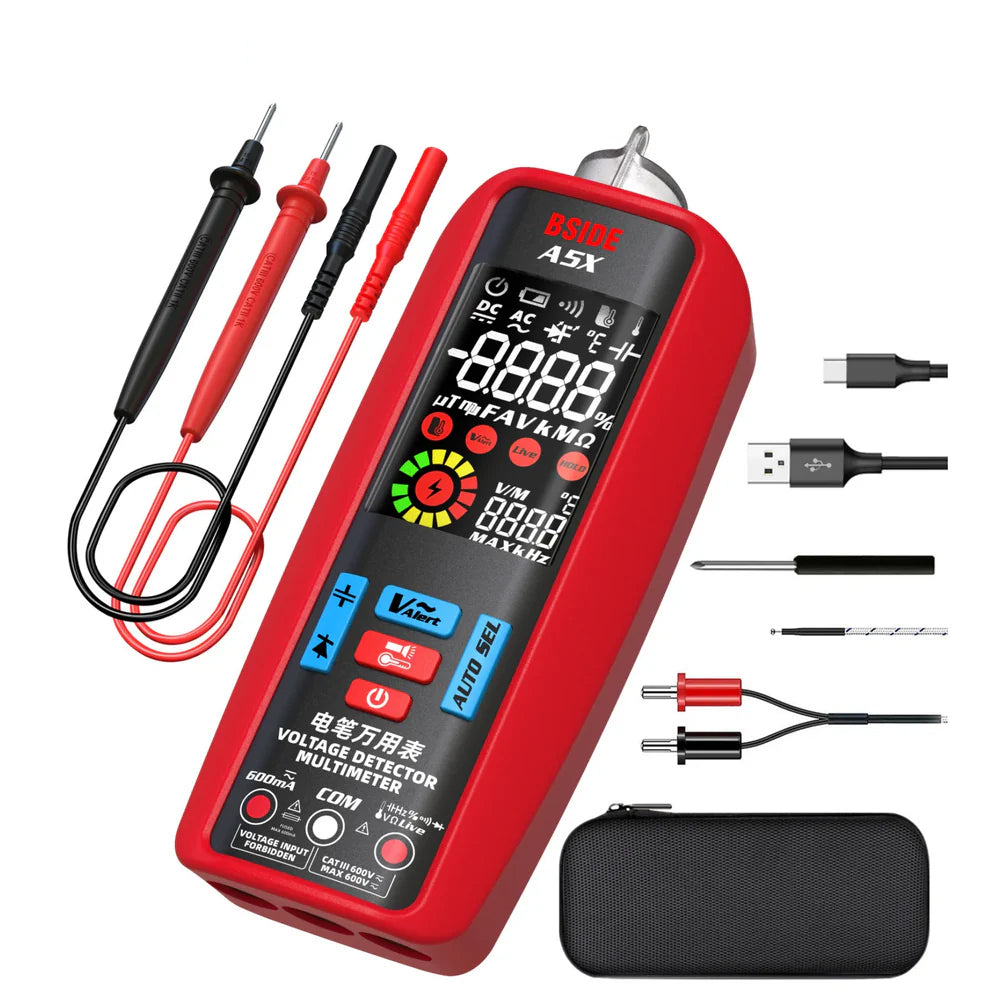
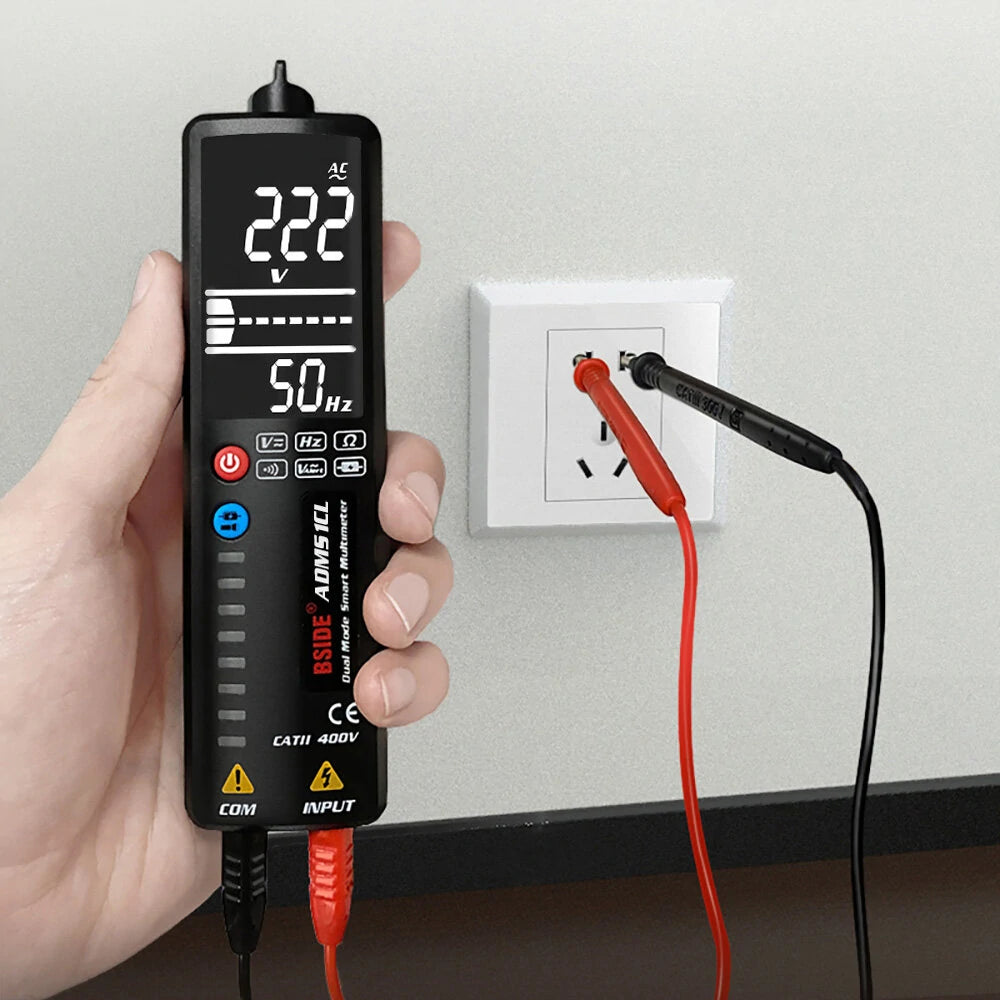
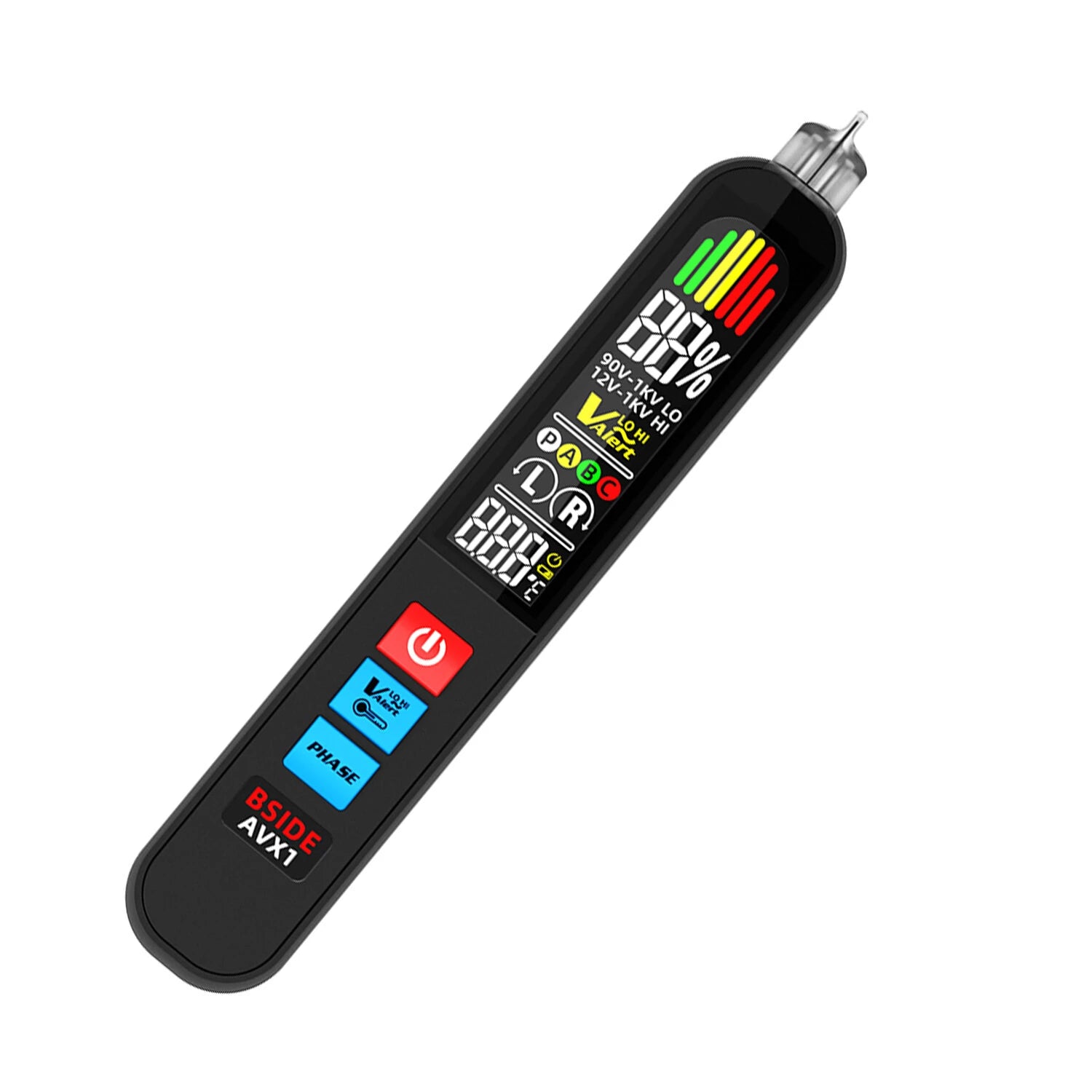
Whether you're a beginner exploring your first DIY electronics project or an experienced technician brushing up, understanding multimeter symbols is essential. These tiny icons on your device tell you what you’re measuring—and using the wrong one could lead to inaccurate readings or even damage.
Let’s break down the most common multimeter symbols and what they mean:
🔋 1. Voltage (V)
-
DC Voltage: ⎓ or a solid line over a dashed line
Measures direct current voltage (batteries, power supplies). -
AC Voltage: ~ or a sine wave symbol
Measures alternating current voltage (wall outlets, appliances).
Tip: Use the right voltage mode for your circuit. Using AC to measure DC can result in misleading readings.
🔥 2. Current (A)
-
DC Current: A⎓
-
AC Current: A~
Many multimeters require moving the probe to a separate port when measuring current. Always check the rating—some meters support only low current.
💡 3. Resistance (Ω)
-
The Greek letter Omega (Ω) represents resistance in ohms.
Used to test resistors, check if a wire is damaged, or ensure a circuit isn't open.
🔄 4. Continuity (🔔 or 📶)
-
Usually marked with a diode symbol or a soundwave icon (🔔)
When enabled, the multimeter beeps if there’s a continuous path.
Perfect for checking if two ends of a wire are connected.
📈 5. Diode Test (▶|—)
-
Looks like a triangle pointing at a line.
Tests whether a diode is working properly by applying a small voltage.
⚡ 6. Capacitance (—|(—)
-
Often shown as two parallel lines with a gap.
Used to test capacitors (measure in microfarads µF).
Make sure capacitors are discharged before testing!
📶 7. Frequency (Hz)
-
Measures frequency in hertz.
Common when working with signal generators or AC power lines.
🌡️ 8. Temperature (°C or °F)
-
Some multimeters have a thermometer mode, usually requiring a thermocouple.
Ideal for measuring surface or environmental temperatures in electronics and HVAC.
🧲 Bonus: BSIDE Multimeters Make It Easy
If you're using a BSIDE multimeter like the SH7, S30, or ZT-M1, the interface is designed to be intuitive. Many models include auto-ranging and symbol labeling directly on the screen to reduce confusion for beginners.
🛠️ Final Tips for Beginners
-
Always start at the highest range and work down when in manual mode.
-
Double-check your probes’ positions—especially when switching between voltage and current.
-
Read the user manual for your specific model (check the BSIDE website for digital versions).
📚 Conclusion
Multimeter symbols don’t have to be confusing. With a little practice, you'll be reading voltage, checking continuity, and testing components with confidence. Bookmark this guide as your go-to multimeter symbol reference.