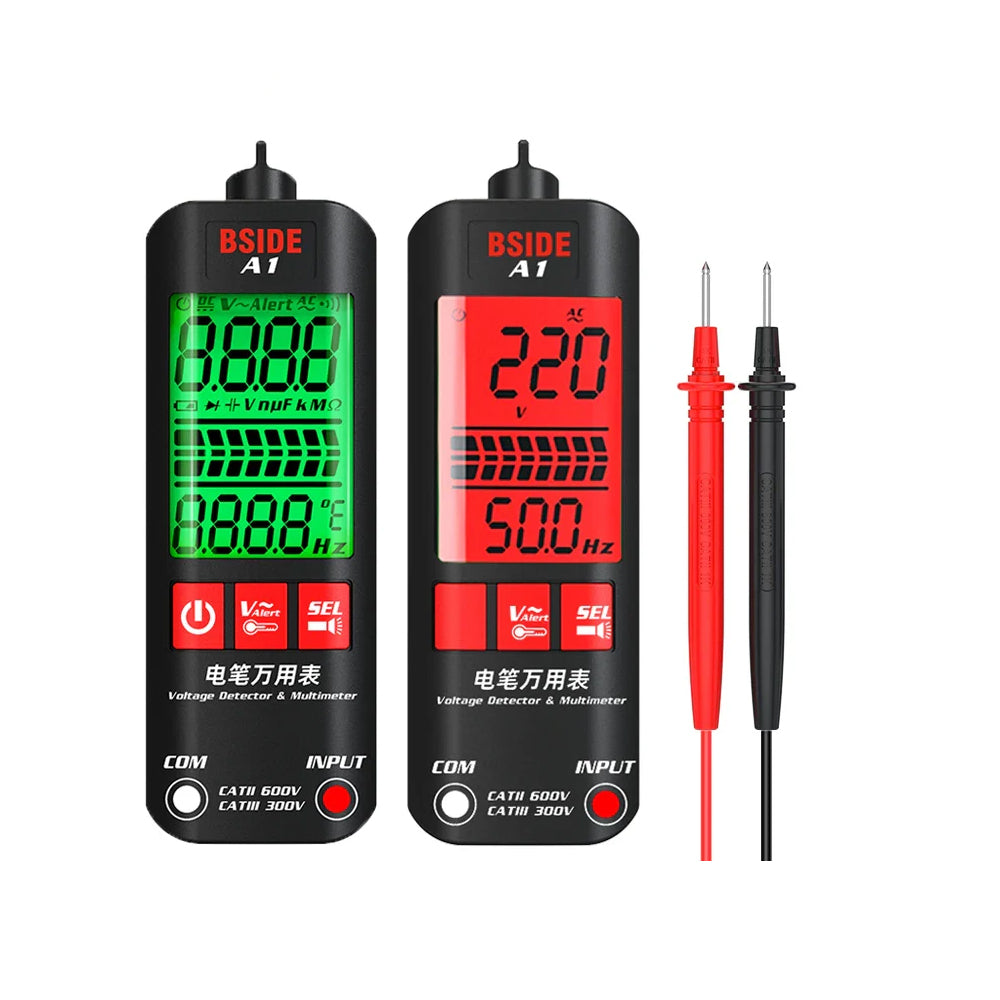
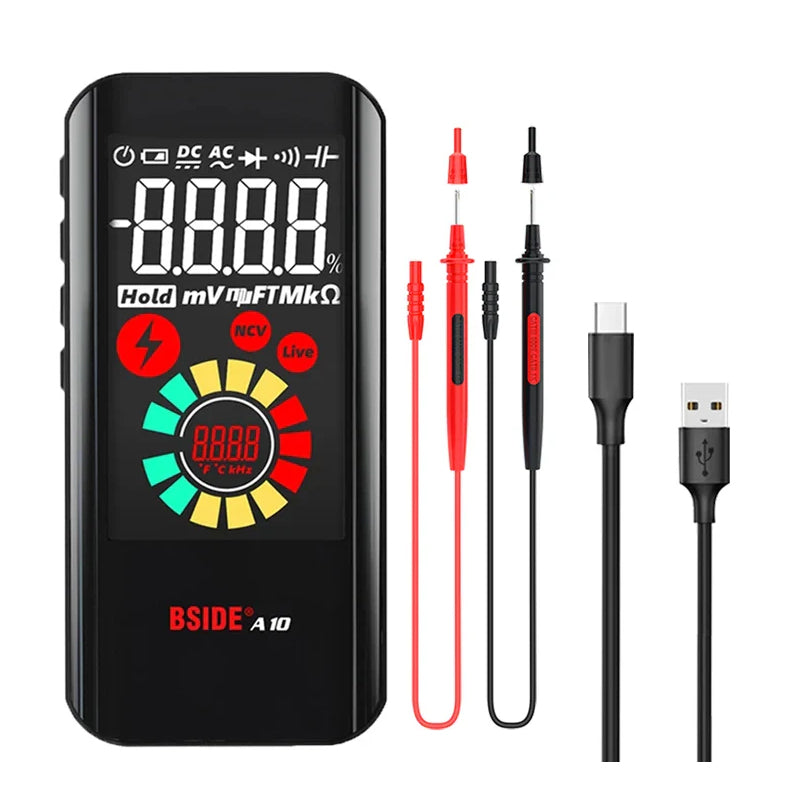
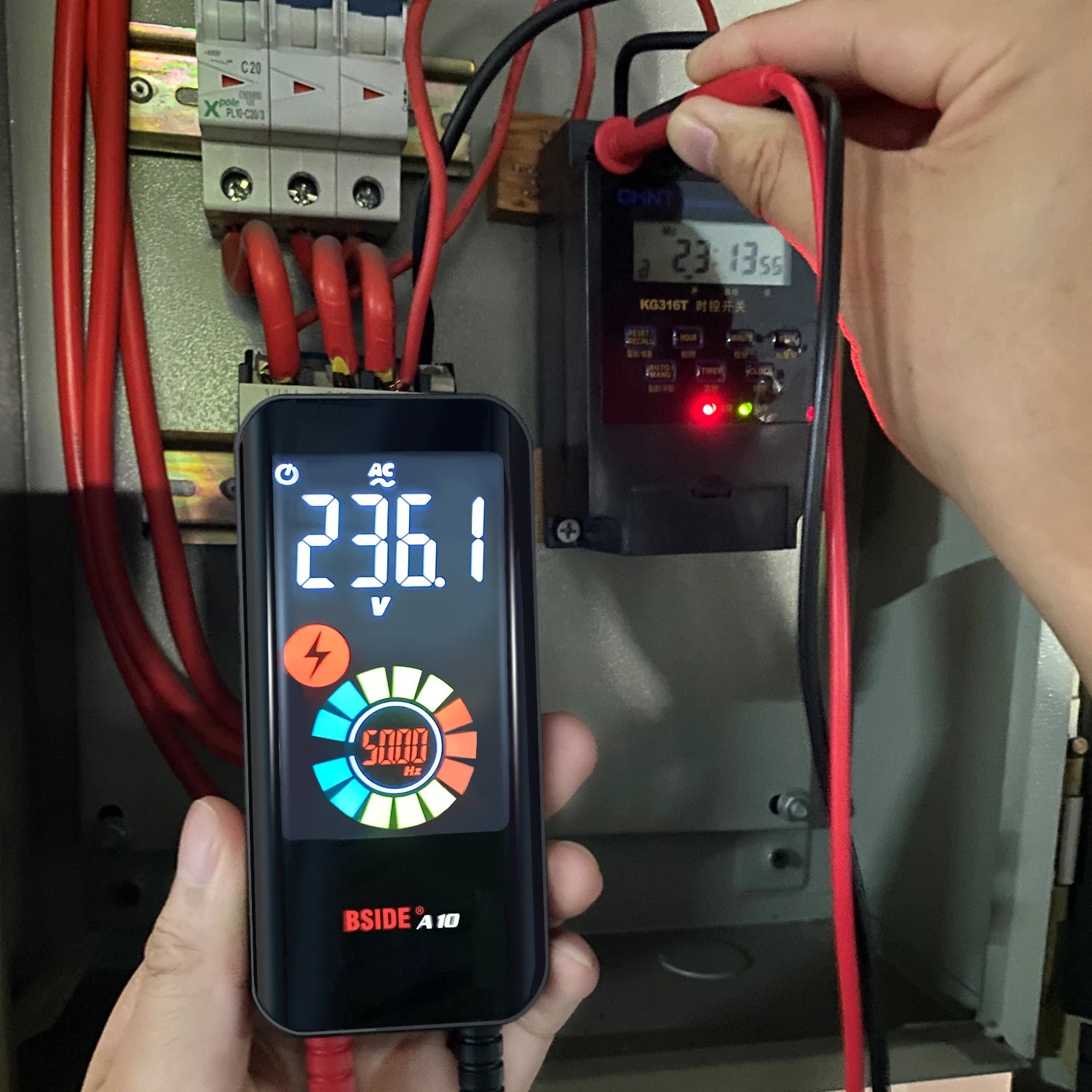
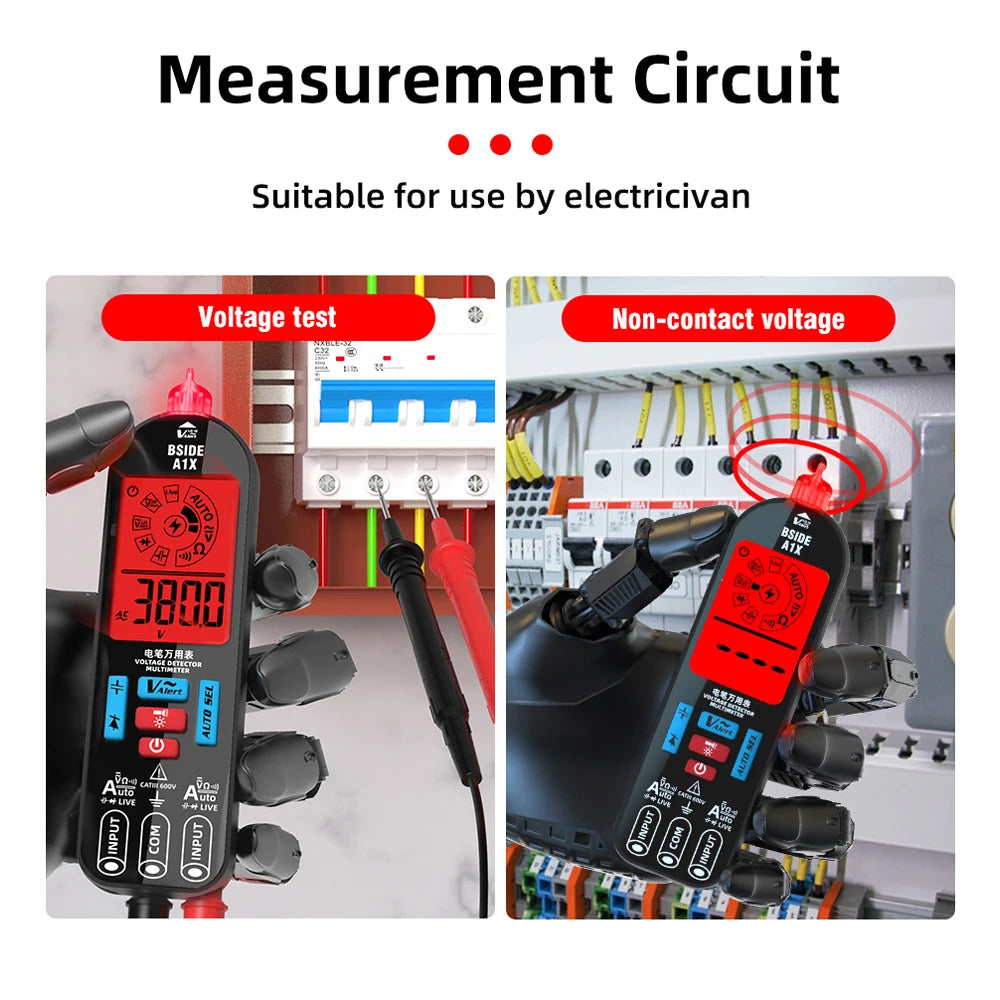
A multimeter is one of the most useful tools for anyone working with electricity. Whether you’re a DIY hobbyist, an electrician, or a technician, a multimeter can help you measure and troubleshoot electrical systems quickly and safely.
But what exactly is a multimeter used for?
Let’s explore the top functions and real-world uses of a digital multimeter (DMM).
📟 What Is a Multimeter?
A multimeter is a handheld device used to measure multiple electrical values—typically:
-
Voltage (V)
-
Current (A)
-
Resistance (Ω)
Modern digital multimeters (like those from BSIDE) also include features such as continuity testing, diode testing, capacitance, frequency, temperature, and even thermal imaging in advanced models.
🔌 What Is a Multimeter Used For?
1. Measuring Voltage
Multimeters can measure both:
-
DC voltage (⎓) from batteries, power supplies, solar panels, etc.
-
AC voltage (~) from wall outlets and appliances
This helps you:
-
Check if a battery is charged
-
Troubleshoot power issues
-
Verify output from a power adapter
2. Measuring Current
By measuring amperage, you can determine:
-
Whether a circuit is drawing too much or too little current
-
If a fuse or component is overloaded
-
How much power a device is consuming
🔧 Some multimeters use probes for current, while clamp meters (like BSIDE ACM91) measure current without disconnecting wires.
3. Measuring Resistance
Used to:
-
Check if a resistor works properly
-
Diagnose broken wires or connections
-
Test heating elements, fuses, or coils
A good reading = low resistance; a bad component = high resistance or “OL” (open loop)
4. Continuity Testing
Quickly checks if a circuit is complete.
-
You’ll hear a beep if electricity can flow through
-
Useful for wiring, switches, and connections
5. Diode and Component Testing
Some multimeters can test:
-
Diodes (directional current flow)
-
Capacitors (store charge)
-
Transistors (amplifiers or switches)
6. Frequency and Duty Cycle
Electricians and engineers use this to:
-
Diagnose AC signals
-
Troubleshoot motor controllers, sensors, and HVAC systems
7. Temperature Measurement
Many advanced multimeters include a thermocouple input to measure temperature, useful for:
-
HVAC repair
-
Electronics
-
Automotive systems
🧰 Who Uses a Multimeter?
Multimeters are essential for:
-
DIYers: Home electrical projects, testing batteries
-
Electricians: Troubleshooting circuits, breaker panels
-
Technicians: Automotive repair, appliance servicing
-
Students: Learning the basics of electronics
-
Engineers: Designing and testing prototypes
💡 Why Choose a BSIDE Multimeter?
BSIDE offers multimeters for all levels:
-
SH7: Smart thermal imaging multimeter for advanced diagnostics
-
S30: Compact, auto-ranging multimeter for daily use
-
S11: Beginner-friendly model with core features and strong durability
All BSIDE meters are:
✅ Accurate
✅ Easy to use
✅ Budget-friendly
✅ Designed with safety in mind (CAT II/III rated)
✅ Conclusion
Multimeters are versatile, must-have tools for anyone dealing with electricity. Whether you're testing a battery, diagnosing a circuit, or learning electronics, a digital multimeter helps you do the job faster and more safely.
Ready to get started?
👉 Shop BSIDE Digital Multimeters