Whether you're troubleshooting electronics, testing a power supply, or checking batteries, understanding how to measure DC voltage (VDC) with a multimeter is essential. This guide will walk you through the steps with practical tips—and we’ll show you why BSIDE multimeters are a smart choice for both DIYers and professionals.
What is VDC?
VDC stands for Voltage Direct Current, the type of electrical flow that moves in a single direction—common in batteries, power adapters, and most electronics. Unlike alternating current (AC), which changes direction periodically, DC is stable, making it crucial to know how to measure it correctly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring VDC
1. Turn the Dial to DC Voltage
Locate the “V” symbol with a straight line (sometimes accompanied by dashed lines) on your multimeter. This indicates DC voltage mode.
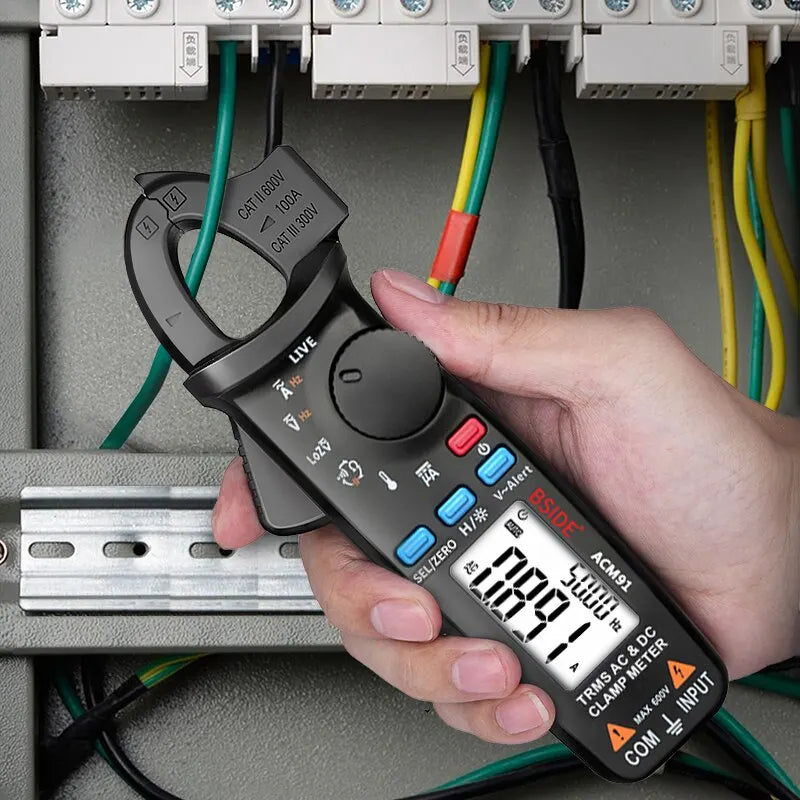
With a BSIDE multimeter like the BSIDE ZT-M1 or the BSIDE S11 Smart Multimeter, simply turn the rotary switch to the V⎓ or DCV position. These models even feature auto-ranging, so you don’t need to guess the voltage range.
2. Plug in the Probes
Insert the black probe into the COM (common) terminal and the red probe into the VΩmA terminal. Always double-check before proceeding.
3. Touch the Probes to the Circuit
-
Touch the black probe to the negative (-) side.
-
Touch the red probe to the positive (+) side.
Your multimeter should now display the voltage reading. For example, a standard AA battery should read around 1.5V DC.
4. Interpret the Reading
-
A positive value means the red probe is on the positive terminal.
-
A negative value means the probes are reversed (no worries, just swap them).
Why Choose BSIDE Multimeters?
When it comes to accuracy, ease of use, and affordability, BSIDE multimeters stand out. Unlike some entry-level models from other brands like Klein Tools or INNOVA, BSIDE offers features like:
-
Auto-ranging detection (no need to pre-select the range)
-
Large backlit LCD screens
-
Live wire detection
-
Compact and rugged designs, perfect for toolboxes or fieldwork
Take the BSIDE ZT-X for example: it not only measures VDC but also offers NCV detection, continuity beeping, and even temperature testing—all at a fraction of the cost of traditional brands.
Pro Tip
Always start measuring with the highest voltage range if you’re unsure of the power source. This avoids accidentally overloading your multimeter.
Common Use Cases for Measuring VDC
-
Checking battery health
-
Verifying voltage from USB ports
-
Testing adapters or wall wart power supplies
-
Diagnosing automotive circuits
Conclusion
Learning to measure VDC with a multimeter is a basic but powerful skill in electronics and DIY repair. With the right tools—like a BSIDE digital multimeter—you can ensure accuracy and safety in your measurements.
Looking for a reliable and budget-friendly multimeter? Explore BSIDE’s latest models today!



Share:
What Does It Mean If a Multimeter Beeps?
What Brand of Multimeter Is Best?